Trehalose is a naturally occurring disaccharide that has become a popular element in the formulation of eye drops to combat dry eyes, a very annoying and increasingly common problem in our modern society.  Used for its osmoprotective properties, trehalose protects epithelial cells on the surface of the eye from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation.
Used for its osmoprotective properties, trehalose protects epithelial cells on the surface of the eye from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation.
However, despite its benefits, it is also important to examine the potential risks associated with the use of trehalose, especially in the form of eye drops. This article offers an in-depth look at how trehalose interacts with the delicate tissues of our eyes, highlighting both the benefits and possible contraindications, to provide a comprehensive overview of this compound that is increasingly present in ophthalmic treatments.
Trehalose: an increasingly used compound
Trehalose is a compound that is increasingly used in the formulation of dietary, cosmetic and pharmaceutical products and in particular is used as an ingredient in the production of eye drops. In this section, we will explore its biochemical profile in these different aspects.
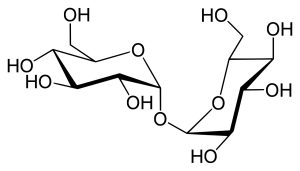 The trehalose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules. Present in nature in organisms such as fungi, yeasts and crustaceans, has the ability to protect cells from drying out. This property is essential in the processes of conservation and stabilisation. It differs from other sugars in its ability to maintain cellular integrityeven under extreme environmental conditions.
The trehalose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules. Present in nature in organisms such as fungi, yeasts and crustaceans, has the ability to protect cells from drying out. This property is essential in the processes of conservation and stabilisation. It differs from other sugars in its ability to maintain cellular integrityeven under extreme environmental conditions.
Its action underlies the natural phenomenon of theanhydrobiosis, i.e. the ability of a living being to survive under extreme thermal conditions and especially persistent drought. The cells of living beings subjected to severe environmental stress and dehydration manage to survive (and recover vitality when rehydrated) precisely because of their ability to synthesise trehalose.
These properties make this sugar very useful in applications ranging from the medical field to the food industry. It is also often used to improve the stability of products during storage and distribution.
Due to its non-reactive nature, it is considered safe for human consumption and this characteristic makes it a popular ingredient in food and pharmaceutical products.
It is important to learn more about all its properties in order to take full advantage of its benefits, but also to assess the risks associated with its intake.
Uses of Trehalose in Industries
Trehalose has applications in various sectors due to its unique properties. In the food industryis used as a sweetener and stabiliser, improving the shelf life and flavour of products. It is often found in baked goods and confectionery.
In the cosmetics industrytrehalose is used for its ability to retain moisture, improving the texture and effectiveness of formulations. It is common in skin care products, offering moisturising and anti-ageing properties.
In pharmaceuticals, trehalose is used to stabilise proteins and vaccines during production and storage. Its ability to protect cells from environmental damage makes it very useful in this context.
 In the medical sector, it is used to improve ophthalmic solutions, such as eye drops.
In the medical sector, it is used to improve ophthalmic solutions, such as eye drops.
This versatility demonstrates the wide range of applications of trehalose in industries.
Benefits of Trehalose for the Eyes
Trehalose offers some ocular health benefits. Its moisturising and protective properties are relevant for those suffering from dry eyes or other forms of ocular discomfort.
Hydration and Visual Comfort
Trehalose is known for its ability to moisturise the ocular surfaceThis is essential for visual comfort, especially in dry environments or after prolonged use of digital devices.
In particular trehalose:
- It retains moisture on the surface of the eye, reducing irritation.
- It helps stabilise the tear film, preventing dryness.
- Improves visual comfort, reducing eye fatigue.
The use of eye drops containing trehalose is proposed to improve the quality of vision of dry eye sufferers. Its ability to retain moisture is particularly useful in air-conditioned or centrally heated environments.
This moisturising effect is supported by studies showing a reduction in irritation and an increase in visual comfort in patients treated with trehalose. The result is clearer and more comfortable vision.
Protection against Free Radicals
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage eye cells. Trehalose offers a effective protection against this damage thanks to its antioxidant properties.
Trehalose works by neutralising free radicals, reducing oxidative stress on eye cells. This is a useful step in preventing degenerative eye diseases, such as retinal diseases like AMD.
The use of trehalose has also been associated with a reduction in ocular inflammation, an important effect as it contributes to long-term support of ocular surface balances, preventing further oxidation damage.
Risks of Trehalose Use
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of trehalose may, however, entail some risks and potential side effects. It is important to be informed about these aspects before starting treatment with trehalose products.
Potential Side Effects
 The use of trehalose, especially in the form of eye drops, may cause some side effects that should not be underestimated.
The use of trehalose, especially in the form of eye drops, may cause some side effects that should not be underestimated.
Although generally safe, some people may experience adverse reactions, which are summarised below:
- Eye irritation: In some cases, eye drops containing trehalose may cause slight irritation or temporary burning.
- Allergic reactions: Although rare, allergic reactions with symptoms such as redness and itching may occur.
- Blurred vision: May occur immediately after the application of eye drops, although usually of short duration.
It is advisable to consult a doctor if you notice persistent or severe symptoms.
In general, early identification of any adverse reactions of an eye drop is crucial for the safe and effective use of the product.
Contraindications and Precautions
There are some precautions to be considered when using trehalose.
- Anyone with a history of allergies to the components of eye drops should always consult a doctor before use.
- Avoid contact of the dropper with external surfaces to prevent contamination.
- Do not use in case of known hypersensitivity to trehalose or any other component of the formulation.
- Consult an ophthalmologist if using other ophthalmic drugs to avoid unwanted interactions.
 These precautions may be helpful in reducing the risks associated with the use of trehalose.
These precautions may be helpful in reducing the risks associated with the use of trehalose.
Trehalose and Microbiota
The role of trehalose in ocular health has been analysed in numerous studies, with a focus on its use in the treatment of dry eye.
This section is, however, specifically focused on the impact of trehalose use on the health of the whole body.
Risk of microbiota imbalances
The increasing use of trehalose in pharmaceuticals, dietary and cosmetic products has raised significant concerns about the alterations that increased intake of trehalose could cause to the microbiota.
The balance of the microbiota is, as numerous studies have shown, the basis for maintaining healthy conditions of the entire organism, but also of the eye and ocular surface in particular.
An important risk is that pathogenic microorganisms exploit trehalose, as well as other sugars, to gain an advantage over normal intestinal microflora.
Research developments will still have to investigate when and how we should regulate our intake of all sugars to preserve our health and, in particular, the delicate balance of the ocular apparatus.
Trehalose and hyaluronic acid
A systematic review, recently published in International Ophthalmology, "Assessing the therapeutic role of trehalose and hyaluronic acid: implications for patient care". analysed through randomised controlled trials in the MEDLINE, PubMed, and Cochrane databases the effects in post-cataract treatment protocols of trehalose, hyaluronic acid and their combination.
The results confirm the positive effects of these treatments in terms of improving the stability and balance of the tear film.
The benefits of Hyaluronic Acid
 L'hyaluronic acidin particular, is a molecule that has been used for many years as an ocular lubricant and re-epithelialiser due to its unique biochemical characteristics.
L'hyaluronic acidin particular, is a molecule that has been used for many years as an ocular lubricant and re-epithelialiser due to its unique biochemical characteristics.
It is in fact a high molecular weight polyanionic polysaccharide with a typical spiral structure that gives it a particular ability to combine with water and an excellent viscoelasticity. This results in an excellent moisturising capacity and a pronounced pseudoplastic behavioursimilar to that of the soluble mucins in the tear film.
On the treatment of dry eye we also suggest
- Cataracts and postoperative dry eye - Oculista Italiano
- Sodium hyaluronate and dry eye after cataract surgery - Oculista Italiano
- Eye pain and dry eye syndrome - Oculist Italiano
- Ballesteros-Sánchez A, Martinez-Perez C, Alvarez-Peregrina C, et al Trehalose and Dry Eye Disease: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 25;12(23):7301. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237301. PMID: 38068353; PMCID: PMC10707449.
- Gawash A, Simonetti A, Lo DF, Shamilov DD, Kumar A, Wong JC. Assessing the therapeutic role of trehalose and hyaluronic acid: implications for patient care. Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 1;44(1):398. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03308-1. PMID: 39352586.
- Buckley A.M., Moura I.B., Arai N., et al. Trehalose-Induced Remodelling of the Human Microbiota Affects Clostridioides difficile Infection Outcome in an In Vitro Colonic Model: A Pilot Study. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021;11:670935. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.670935
- Buckley A.M., Moura I.B., Wilcox M.H. Is there a causal relationship between trehalose consumption and Clostridioides difficile infection? Opin. Gastroenterol. 2021;37:9-14. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000695.
