Eyelid dermatitis is a skin disorder that can affect all types of patients, causing discomfort and irritation in the delicate area around the eyes. Understanding the causes of this pathological condition is key to effectively managing it and improving the quality of life of sufferers. Symptoms vary from mild redness to intense itching, affecting appearance and daily comfort. Fortunately, there are effective treatments that can alleviate symptoms and prevent future episodes. In this article, we will explore the most common causes, signs and treatment options available for eyelid dermatitis, offering practical advice 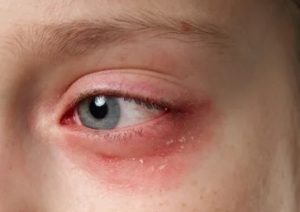 to deal with it safely.
to deal with it safely.
Causes of Eyelid Dermatitis
Eyelid dermatitis can be triggered by many factors, some more frequent than others. Identifying the specific causes is essential to prevent and effectively manage this pathological condition.
In this section, we will explore environmental factors, allergic reactions and genetic predispositions.
The periocular area
The term periocular area means all that area surrounding the eyes. The skin in this space is very different and has special characteristics and, above all, special needs. It is very delicate: the skin is 10 times thinner than that of the rest of the face.
Common Environmental Factors
I environmental factors can play a significant role in the development of eyelid dermatitis. Elements such as pollution, cigarette smoke and dust can irritate the sensitive skin of the eyelids.
- Exposure to harsh chemicals, such as detergents, can cause irritation.
- Climatic changes, such as excessive wind or humidity, can exacerbate symptoms.
- The use of unsuitable cosmetic products can aggravate the situation.
Taking preventive measures, such as using appropriate protection and choosing hypoallergenic products, can reduce the impact of unfavourable environmental situations.
Allergic reactions
Le allergic reactions are a frequent cause of eyelid dermatitis.
Allergens such as pollen, animal hair and food can cause skin reactions on the eyelid.
A few suggestions:
- Avoid contact with known allergens.
- Use fragrance-free products to reduce the risk of sensitisation.
- Consider the use of antihistamine treatments.
Speaking of allergies, keeping a diary of periocular skin reactions can be helpful in identifying specific triggers.
Genetic Predispositions
Some people may have a genetic predisposition to develop dermatitis. A family history of skin problems is often an indicator here.
- Atopic dermatitis is often hereditary.
- Genetic mutations can affect the function of the skin barrier.
- The presence of close relatives with dermatitis increases the risk.
Understanding the genetic and hereditary component can help plan preventive strategies and customise treatments to improve quality of life.
Main Symptoms
Symptoms of eyelid dermatitis can vary, but often include irritation, redness and itching. Recognising these signs is crucial for timely and effective treatment.
 Irritation and redness
Irritation and redness
L'irritation and the redness are among the most common symptoms of eyelid dermatitis. These symptoms may manifest themselves as mild inflammation or noticeable redness.
- The redness may be localised or diffuse over the entire eyelid.
- Irritation may worsen with repeated contact with triggers.
- Relieving the irritation with cold compresses can be helpful.
Identifying the causes and adopting strategies to reduce exposure to irritants can alleviate these symptoms.
Persistent itching
The itching is a persistent symptom that can cause considerable discomfort. It is often accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Scratching can further damage the skin.
- The use of soothing creams can reduce itching.
- Avoiding contact with irritants is essential.
Early intervention can prevent complications and improve daily comfort.
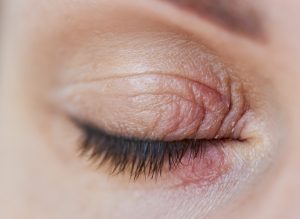
Skin Dryness
La dryness is a common symptom accompanying eyelid dermatitis. Dry skin may flake and cause further irritation.
Some useful tips:
- Apply moisturising creams regularly.
- Use humidifiers in dry environments.
- Drink adequate amounts of water to maintain hydration.
Constant skin moisturisation strategies help reduce dryness and improve elasticity.
Diagnosis of Dermatitis
Diagnosing eyelid dermatitis requires a methodical approach to identify the underlying cause.
There are tests and consultations that can help clarify the situation.
Dermatological examinations
The dermatological examinations can be helpful in determining the presence and severity of eyelid dermatitis.
- A visual examination of the skin may reveal specific signs.
- Analysis of the skin tissue may provide further details.
- Professional evaluation is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Early diagnosis improves the chances of effective treatment.
Allergy Testing
I allergy tests are useful for identifying the allergens responsible for skin reactions.
- Skin tests can identify the cause of immediate reactions.
- Blood tests can detect systemic allergies.
- Consultation with an allergist can clarify the overall situation in the body.
These tests are very useful in identifying specific triggers, allowing for more targeted treatments.
Medical Consultations
Le medical consultations with specialists are essential to customise the treatment of eyelid dermatitis.
- Regular visits help to monitor the progress of the therapy.
- Experts may suggest modifications to the therapy.
- In-depth discussions improve understanding of the pathological condition.
An ongoing relationship with the doctor guarantees a customised approach and constant treatment updates.
Effective Treatments
Several treatments can alleviate the symptoms of eyelid dermatitis. From natural solutions to medication, there are options for every need.
Natural Remedies
I natural remedies can offer relief from the symptoms of eyelid dermatitis without side effects.
Some examples:
- Aloe vera is known for its soothing properties.
- Chamomile compresses can reduce skin inflammation.
- Coconut oil keeps the skin moisturised.
Regular use of natural remedies can greatly improve skin health.
Pharmacological Treatments
I pharmacological treatments include creams and ointments based on corticosteroids or antihistamines.
- Steroid creams reduce inflammation.
- Antihistamines relieve itching.
Medicines should always be used under medical supervision.
A targeted pharmacological approach can provide rapid and effective relief.
Prevention Therapies
Le prevention therapies are essential to reduce the frequency of eyelid dermatitis episodes.
- Avoiding known triggers is crucial.
- The use of hypoallergenic skin products can prevent reactions.
- Maintaining a skin care routine helps prevent recurrences.
Taking preventive measures can limit episodes and improve quality of life.
Prevention Tips
Preventing eyelid dermatitis requires care and a proactive approach. Following practical advice can reduce risk and improve general well-being.
Daily Skin Care
A daily skin care appropriate is essential to prevent eyelid dermatitis.
Some rules that should be followed:
- Gently cleanse the skin around the eyes with appropriate products.
- Moisturise the eye area regularly to maintain its elasticity.
- Protect the skin from UV radiation with sunscreens.
Proper skin care habits reduce the risk of skin irritation episodes.
Identification of Triggers
Identify the triggers is essential to prevent skin reactions.
There are some indications that may be useful to know in this area:
- Keep a reaction diary to identify patterns.
- Experiment with the elimination of potential allergens.
- Consult specialists for specific tests.
Knowing your triggers allows you to manage eyelid irritation effectively.
Lifestyle Changes
Sometimes, simple lifestyle modifications can make a difference in the management of eyelid dermatitis.
- Reducing stress helps to reduce skin reactions.
- Avoiding polluted environments can prevent irritation.
- A balanced diet supports healthy skin.
Daily lifestyle adjustments and corrections can significantly improve the control of eyelid dermatitis.
- Rubegni G, Padula T, Calabrese L, D'Onghia M, Tognetti L, Cinotti E, Lazzeri L, Ermini G, Cartocci A, Tosi GM. Eyelid Contact Dermatitis: 25-Year Single-Centre Retrospective Study. J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 27;14(3):823. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030823. PMID: 39941494; PMCID: PMC11818699.
- Valsecchi R., Imberti G., Martino D., Cainelli T. Eyelid Dermatitis: An Evaluation of 150 Patients. Contact Dermat. 1992;27:143-147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb05242.x.
- Svensson A., Möller H. Eyelid Dermatitis: The Rôle of Atopy and Contact Allergy. Contact Dermat. 1986;15:178-182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.1986.tb01321.x.
