Cataracts, the loss of transparency that occurs in the crystalline lens (or natural lens of the eye), are the leading cause of blindness in the world. For this reason, in 2016 thehe Italian Ophthalmological Society (SOI) and the Italian Association of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (AICCER) have set up a national working group to update the Clinical-organisational guidelines on cataract surgery. The overriding aim of these recommendations was to meet the needs of patients and improving quality of their lives, while ensuring their safety and that of their caregivers. The review carefully evaluated and compared clinical practice in our country with the cataract guidelines of the American Academy of Ophthalmology, the Royal College of Ophthalmologists, the Canadian Ophthalmological Society and the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. These analyses and comparisons resulted in the following guidelines on both the diagnosis and treatment of cataracts.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of cataract requires a thorough ophthalmic examination to assess the health of the eye and the degree to which visual function is impaired.
This usually includes:
– general anamnesisbased on a document drawn up by the general practitioner;
– ophthalmic anamnesisbased on the patient's ophthalmic medical history;
– objective examinationwhich analyses the anatomical state of the visual apparatus with particular attention to all elements that may be relevant to surgery (presence of ocular pathologies associated with cataracts, dilatability of the pupil, exportability of structures posterior to the crystalline lens);
– functional examinationfor the detection of distance and near vision with the best optical correction;
- biometrics;
- possible selection of the intraocular lens (IOL), in the case of surgery, according to the needs of the patient and the refractive status of the contralateral eye.
Treatment
Non-surgical
Although cataract is ultimately a surgical condition, there are several non-surgical treatment options that can temporarily optimise visual function. The ophthalmologist can, in fact, prescribe new glasses to correct refractive changes related to changes in crystalline lens opacity, while for specific reading difficulties it may help to increase ambient lighting or increase the power of the bifocal portion of the glasses. To date, the scientific literature does not support evidence of a benefit of nutritional supplements in preventing or delaying cataract progression and there is no medical treatment to treat or permanently reverse cataract formation.
Surgical
Cataract surgery consists of removing the opacified lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens. The artificial lens, called an intraocular lens (IOL), is placed in the same position as the natural lens, remaining a permanent part of the eye. 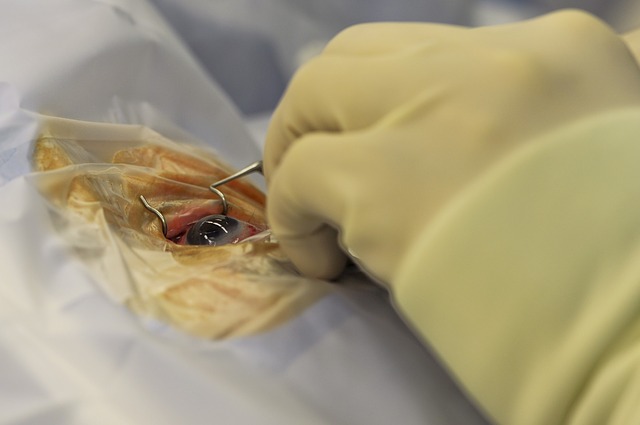 The main indication for cataract surgery is the patients' desire to improve their visual function and the possibility that cataract surgery will help them achieve this goal.
The main indication for cataract surgery is the patients' desire to improve their visual function and the possibility that cataract surgery will help them achieve this goal.
Cataract surgery is indicated:
- to improve the visual function of individuals with cataracts and also with other eye diseases;
- in order to make better use of the functional residue of visually impaired individuals for other serious eye diseases;
- in order to accurately explore the posterior segment of the eye;
- to prevent the development of other eye diseases.
Current cataract surgery is performed under topical/local anaesthesia and on an outpatient basis. The operation is generally performed in one eye at a time even when the pathology is bilateral, but the presence of particular conditions (systemic or ocular) may make surgery in both eyes in the same surgical session useful.
Cataract surgery techniques
The 3 main cataract surgery techniques are: intracapsular lens extraction, extracapsular lens extraction and phacoemulsification.
Intracapsular extraction consists of removing the entire lens including the capsule, after which the patient has to wear special (aphakic) spectacles because no synthetic lens is implanted. This procedure is no longer used in developed countries except in rare cases (partially displaced lenses).
Extracapsular cataract extraction involves the removal of the opacified lens as a whole, but leaving the capsule and zonular attachments intact, so as to have a scaffold for the implantation of a synthetic lens. Although this method allows the implantation of an IOL, it involves a large incision at the corneal-scleral junction requiring sutures for closure and a longer recovery for the patient. Complication rates are also much higher than with phacoemulsification.
Phacoemulsification is currently the most commonly used procedure for cataract extraction. This procedure involves emulsifying the lens nucleus within its capsule using an ultrasonic probe inserted through a small incision (1.8-3.0 mm). If performed correctly, the small wound size is self-sealing and there is no need for a suture. The advantages of phacoemulsification over regular extracapsular extraction are: smaller incision; lower intraoperative complication rates; shorter procedure time; and faster patient visual recovery time. As with the extracapsular approach, the capsular bag is retained, allowing easy placement of a synthetic lens implant. Despite the rapid recovery and rare complications of phacoemulsification, the eyes are generally operated on separately and done 1-4 weeks apart.
The only exclusion condition for cataract surgery, set out in the guidelines, states that 'cataract surgery should not be performed in the following cases:
- the patient or his guardian is unable to provide informed consent for surgery under elective conditions'.
Sources
–Clinical and Organisational Guidelines on Cataract Surgery. SOI - Italian Ophthalmological Society. 2016
– Cataracts. Thompson J, Lakhani N. Prim Care. Sep;42(3):409-23. 2015.
– Cataracts in adults: management. NICE guideline. 26 October 2017.
Dr. Carmelo Chines
Direttore responsabile
